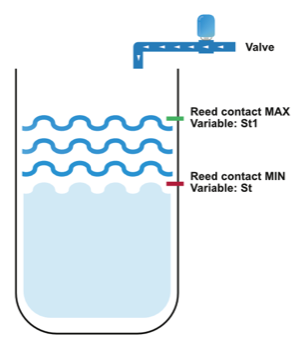
The following example shows how to configure the filling of a retention tank based on measurements of the minimum and maximum water levels.
Configuration using two equations
An alternative solution uses two separate Smart Rules of type Equation – one for turning the valve on and the other for turning it off.
1. Smart Rule: “Turn on the valve”
Variables- MinLevel (Status contact for the minimum level)
- MaxLevel (Status contact for the maximum level)
- Valve (Current state of the valve)
| |
- Valve … Turn on
Explanation: When the level falls below the minimum level (MinLevel = FALSE), the equation !MinLevel returns TRUE and the valve turns on.
2. Smart Rule: “Turn off the valve”
Variables- MaxLevel (Status contact for the maximum level)
| |
- Valve … Turn off
Explanation: When the level reaches the maximum level (MaxLevel = TRUE), the valve turns off.
Configuration using LastState
Variables
- Status contact for the minimum level (Variable name: MinLevel)
- Status contact for the maximum level (Variable name: MaxLevel)
Output devices
- Digital output to control the valve or pump (Name: Valve)
The Equation Smart Rule has an internal variable named LastState. This variable returns TRUE or FALSE based on the last evaluation result of this Smart Rule.
Equation
| |
Actions
If result is TRUE, perform following actions:- Valve … Turn on
If result is FALSE, perform following actions:
- Valve … Turn off
Duration
Minimum duration … 0:05:00 minutes
Configuration with analog level measurement
If you have an analog level measurement available (e.g., an ultrasonic sensor measuring the distance from the bottom of the tank), you can use a more elegant solution with the HYSTERESIS function and a Smart Rule of type Formula .
Variables
- Analog measurement of the level (Variable name: Level) – distance from the bottom of the tank in cm
Output devices
- Digital output to control the valve or pump (Name: Valve)
Configuration using Smart Rule Formula
The Formula Smart Rule automatically assigns the calculated value to the output device.
Formula | |
Parameters of the HYSTERESIS function:
Level– current level height in cm (analog input)90– upper bound in cm (when the level reaches 90 cm, turn off the valve)20– lower bound in cm (when the level falls below 20 cm, turn on the valve)0– output when the upper bound is reached (off)1– output when the lower bound is reached (on)Valve– last value (state memory for hysteresis)
Explanation: The HYSTERESIS function ensures that the valve turns on when the level falls below 20 cm and turns off only when the level reaches 90 cm. Between these values, the valve remains in its last state, thus preventing frequent switching.
More information about the HYSTERESIS function can be found in the scripting language documentation (/sk/documentation/scripting_language/#hysteresis).